What Is Aspherix®?
Aspherix® is a
state-of-the-art Discrete Element Method (DEM) software that provides
comprehensive simulation tools for a wide range of applications.
What Is Aspherix®?
Aspherix is a sophisticated data management and simulation platform featuring state-of-the-art DEM (Discrete Element Method) software. It offers unparalleled control over your data and the ability to simulate particle behavior in various environments and processes, enhancing operational optimization and driving product innovation.
High-Performance DEM Software
Aspherix® is a cutting-edge Discrete Element Method (DEM) software designed to simulate particle behavior in diverse systems, offering high-precision process modeling. It integrates data from multiple sources, ensuring seamless analysis across varied formats.
With user-friendly dashboards, it delivers real-time analytics for instant insights, enabling quick, data-driven decision-making.
High-Performance DEM Software
Aspherix® is a cutting-edge Discrete Element Method (DEM) software designed to simulate particle behavior in diverse systems, offering high-precision process modeling. It integrates data from multiple sources, ensuring seamless analysis across varied formats. With user-friendly dashboards, it delivers real-time analytics for instant insights, enabling quick, data-driven decision-making.
Flexible Licensing, Multi-Platform, Tailored to You — Fast
With flexible licensing, choose between lease or perpetual models, install on unlimited devices, and scale users freely — even mix license types to handle peak demand.
Run Aspherix® and CFDEM®coupling anywhere: Windows or Linux, on desktops, workstations, HPC clusters, or in the cloud.
Need something unique? Our solutions are highly customizable — we deliver custom developments and workflows to fit your exact needs.
Stay ahead with our rapid deployment: two major releases per year plus agile solver updates keep you up to date without IT headaches.
Why Choose Aspherix®?
Efficiency
Benefit from automated data management.
Accuracy
Minimize errors and improve data quality.
Innovation
Enhance processes and drive development.
Support
Use our resources and dedicated support.
Discover Our Capabilities
Ovito
So far the following features are available: Particle representation + coloring according to desired quantities (velocity, …) Efficient representation of nonspherical particles Mesh representation + coloring according to selected properties Representation of particle-particle contact networks Visualization of eulerian fields Pathlines
Electrical Conductivity
Calculation of electric conductivity also available in Aspherix®. Potential & electric heating can be calculated for the particles. Conductance and current can be calculated for all particle-particle and particle-wall contacts. Tutorial case for electric conductivity available!
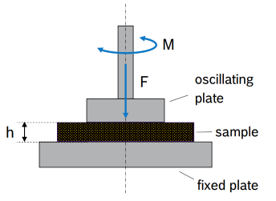
6-DOF Geometry Motion
The geometry of the rigid body is imported as a surface mesh from an STL file. Mass, center of mass and moments of inertia are specified in the according mesh module. External forces,including particle-wall forces determine the geometry motion. 6-DOF plate motion This video shows the motion of a plate around a central hinge. The body rotation is determined by the particle-wall forces and by an external torque that acts in opposition to the rotation around the hinge.
Particle Drying
Moist particles are heated up by warm flow. This leads to a drying of the particles.
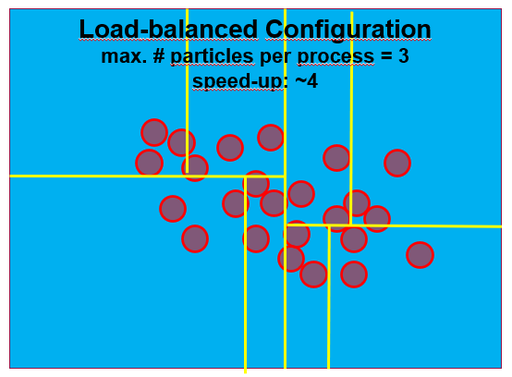
Load Balancing
For an optimal usage of the computational resources it is crucial to distribute the load evenly on all available processes. With the RCB loadbalancing approach it is possible to cut the domain indepently in all directions such that each slice holds equal numbers of particles (see sketch).
Laser Modelling
Heating of a parabolic mirror due to laser reflection. The laser beam is modelled by distinct photons.
Spray Modelling
Using Lagrangian particles for spray coating of a moving meshed object.
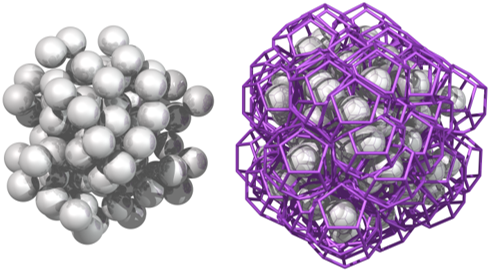
Coarsegraining
In coarsegraining we represent groups of particles by single, larger particles while at the same time we maintain the original properties of the bulk material. This requires scaling laws. In the animation we are comparing the original simulation (3700 particles) to two cases with less, larger particles (462). In the “enlarged” case we simply use larger particles with the same material properties as the original material, in the “coarse-grained” case we apply the required scaling laws. A comparison of the wear on the chute shows that the results for the original and the coarsegrained case match while the “enlarged” case shows strong deviations.
FE Coupling
Interaction between granular material and a deformable chute.
Magnetic Particles
Application case – magnetic separation of particles. The conveyor belt transports particles into magnetic region – particles with strong dipole are separated (depending on their position within the particle bed).
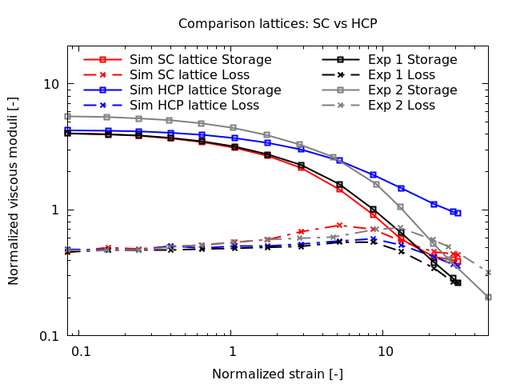
Rheology Models
Aspherix® can simulate materials with rheological models to match storage and loss modulus in oscillatory rheometer tests.
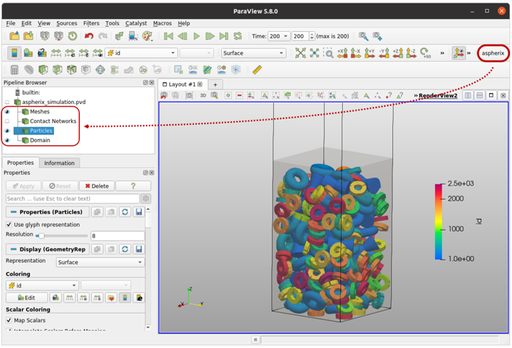
Paraview
Paraview macros are provided for automated postprocessing. When using the “Start Paraview” button in the GUI the data is postprocessed automatically. Alternatively, if the “aspherix_simulation.pvd” file is loaded manually, the “aspherix” macro can be applied for automated postprocessing.
Unresolved Breakage
* Improved model version: elastic energy is disspated * Improved comparison of trajectories * Improved model version: elastic energy is disspated * Improved comparison of trajectories * Center of mass for particles nearly indentica
Particle Insertion
The new insertion command:
1) can insert more (elongated) particles within a region in new packing generator mode batch
2) requires less mandatory keywords
3) accepts the definition of insertion shapes without meshes.
The new packing generator introduces the following functionalities:
1) Insertion of particles across processor boundaries
2) Creation of identical insertions for any processor count or layout
One-Way CFD Coupling (Transient)
Using 1-way coupled Aspherix®-DEM and CFDEM®coupling simulation with a transient fluid velocity field, we are able to model motion of the chaffer inside a combine harvester. Straw and wheat is inserted as a stream from the top and due to segregation and sieving these are separated. The shape and orientation of the particles determines their drag force.
6-DOF Geometry Motion
The geometry of the rigid body is imported as a surface mesh from an STL file. Mass, center of mass and moments of inertia are specified in the according mesh module. External forces,including particle-wall forces determine the geometry motion. 6-DOF plate motionThis video shows the motion of a plate around a central hinge. The body rotation is determined by the particle-wall forces and by an external torque that acts in opposition to the rotation around the hinge.
Soil Models
Calibration of compacted soil with a moisture of 13% using the vane shear test. The approach is based on literature (Karmakar & Kushwaha, 2007).
Defeaturing
- Industrial applications heavily uses meshes
- Handling of meshes of mediocre quality is crucial for industrial applications
- We added an algorithm for automatic removal of small features
Cohesive Mixing
Mixing simulation of cohesive (right) and non-cohesive (left) material. In this project we investigated the mixing efficiency of the geometry, the change of the mixing efficiency for different materials (see graph in video), the residence time distribution and design questions of the mixer geometry.
Wear
The animation shows the deformation of the mesh caused by wear. The Finnie wear model was used to predict the deformations.
Heattransfer
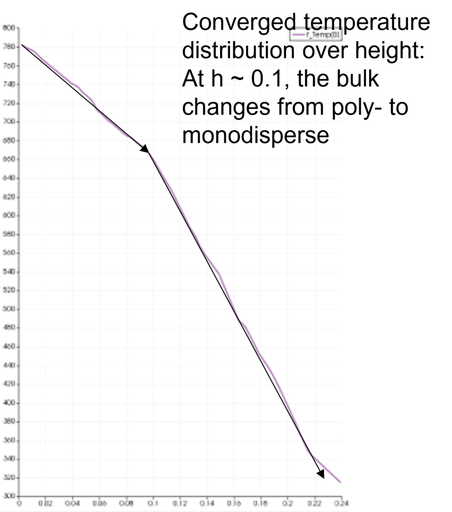
Effect of segregation on heat transfer (link). Top: constant temperature of 300 K adiabatic walls Bottom: constant temperature of 800 K
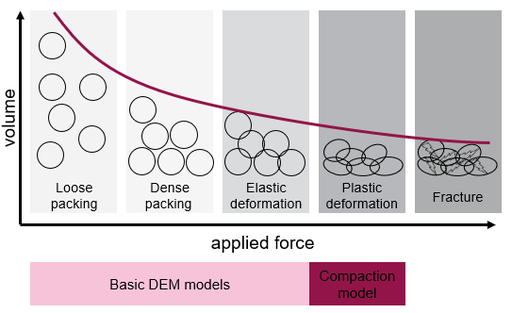
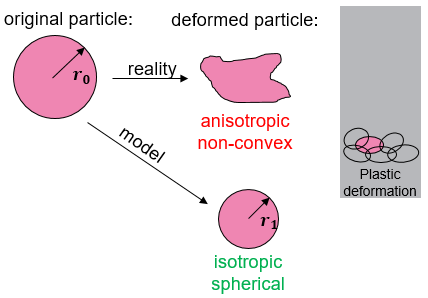
Powder Compaction
Powder compaction is the extension of Aspherix® towards high plastic deformation. For powders, we need a model that is valid all the way from “fluffy agglomerates” to densified tablets.
Energy Evaluation
Analysis of the energy used to lift a bowl out of a packed bed.
One-way CFD with Heat Transfer
Cooling of particles in a rotating drum with counter-current gas flow. The material consists of facetted nonspherical particles and the gas flow is modelled by importing a flow field into Aspherix®.
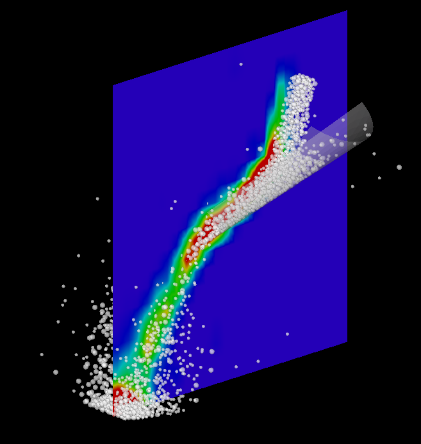
Force Chains
Visualization of the contact forces between particles and particles (center) and particles and walls (right).
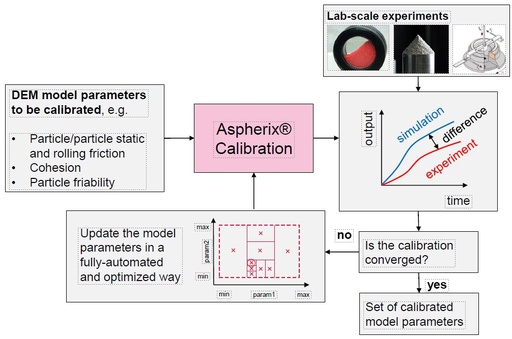
Calibration
Overview of the calibration workflow of Aspherix® Calibration.
Nonspherical Shapes
Aspherix® GUI provides several tools & helpers to generate nonspherical particles. One example is the superquadric builder, which visualizes the particle during its creation and adds it to the simulation automatically:
Job Queue
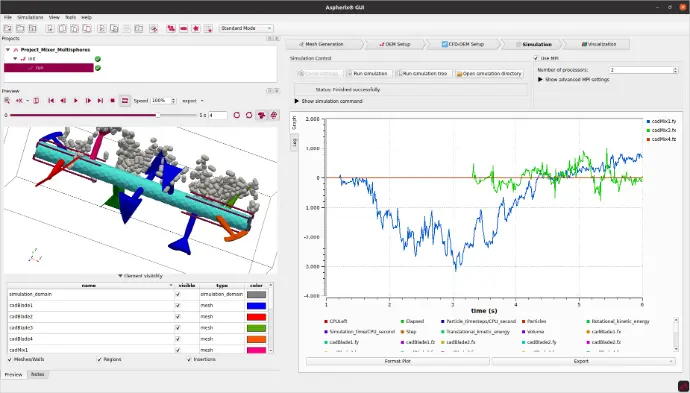
Running a simulation tree with a single click!
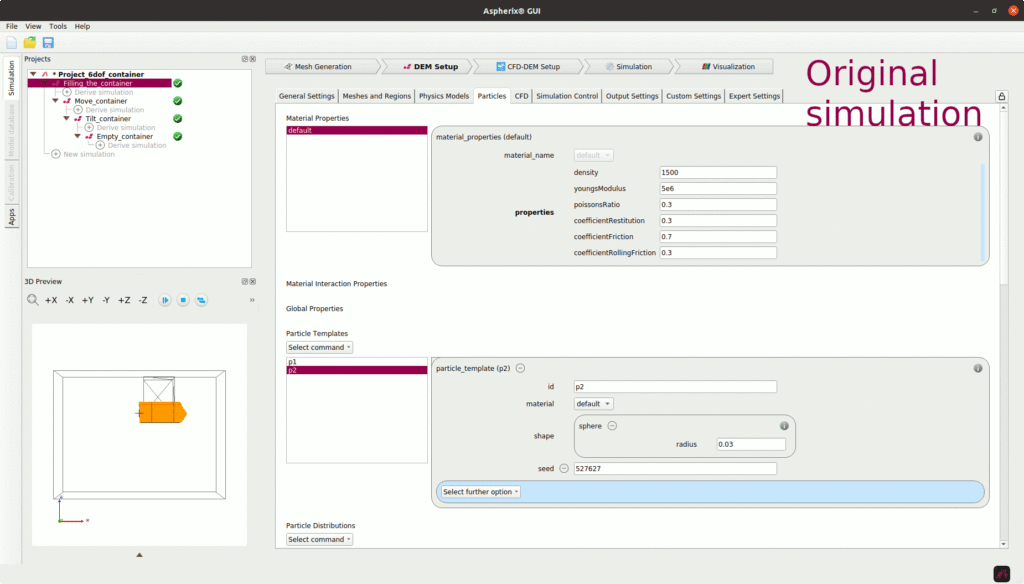
Generating a Coupled Simulation with the GUI
Using the CFD-DEM tab of the GUI to combine a DEM and a CFD case.
Residence Time
KPIs like residence time distributions from processes which take hours used to be inaccessible to highly resolved DEM simulations – now they are accessible!
Appification
With the Appification functionality Aspherix® GUI users can create Apps out of their simulations that can be applied with almost no specific knowledge about DEM or Aspherix®. Only few parameters that should be varied are visible, all other settings are hidden (can be edited in “non-App-view” at all times but are invisible to App users).
Voronoii
Aspherix can compute the Vornoii tesselation of packings, for meshes wall handling is available.
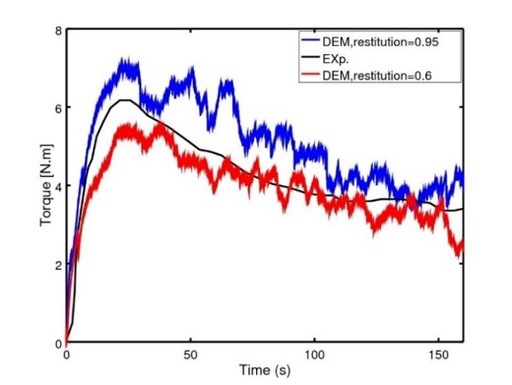
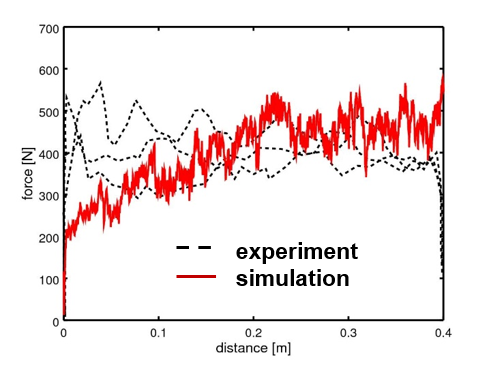
Power Draw
Aspherix® can determine power draw on static and moving parts! Optimize the actuation, operating conditions and geometry of your equipment.
One-Way CFD-DEM with Moving Reference Frame (MRF)
Animation of simulation with one-way CFD-DEM with MRF
Superquadrics
Filling and emptying of a cylinder with superquadric particles.
Spheres
Many bulk materials can be represented by spheres, particularly when using physical models such as rolling friction or cohesion.
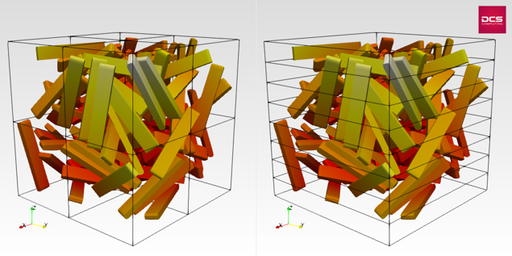
Triangulated
Simulation with A and X shaped particles in a rotating drum. The usage of concave particles allows for an accurate representation of the bulk material.
Multispheres
Investigation of the shape effect in an emptying hopper. On the left hand side, a polydisperse packing of spheres is considered, while the bulk material on the right hand side consists of multisphere particles.
Fibers
In Aspherix®, fibers are modelled as multi-sphere bodies with elast-damping interparticle forces (normal and tangential). In this case, grass, modelled by fibers, is bended by a rotating wheel. After being bent, the fibers tend to move back to their original configuration due to the interparticle forces.
Flexible Membrane
This video shows a flexible membrane that consists of spherical particles. This is a specific application case of a cohesion model.
Bonded Particles
Bonded particles can be used to generate custom shapes like pellets, ellipsoids etc. The mechanical properties of the assemble depend on the bond breakage criterion, normal and tangential stiffness of the bonds, energy dissipation of the bonds and properties of the spherical particles.
Ready to unlock the full potential of Aspherix®?
Request your free 4-week trial, complete with a user-friendly GUI, 16 parallel licenses, and a step-by-step video tutorial to get started!
Power Your Particle Research With Aspherix®
Cutting-Edge Simulation and Data Management for Education
What is Aspherix® Academic?
Are you a researcher looking for the right DEM software for your particle simulations? Aspherix® Academic is the licensing scheme for you! Aspherix® is available under commercial license and consists of a large set of new and cutting edge features:
- Full Aspherix® functionalities
- Project-tailored customization
- Competitive pricing
More To Know About Our Solutions
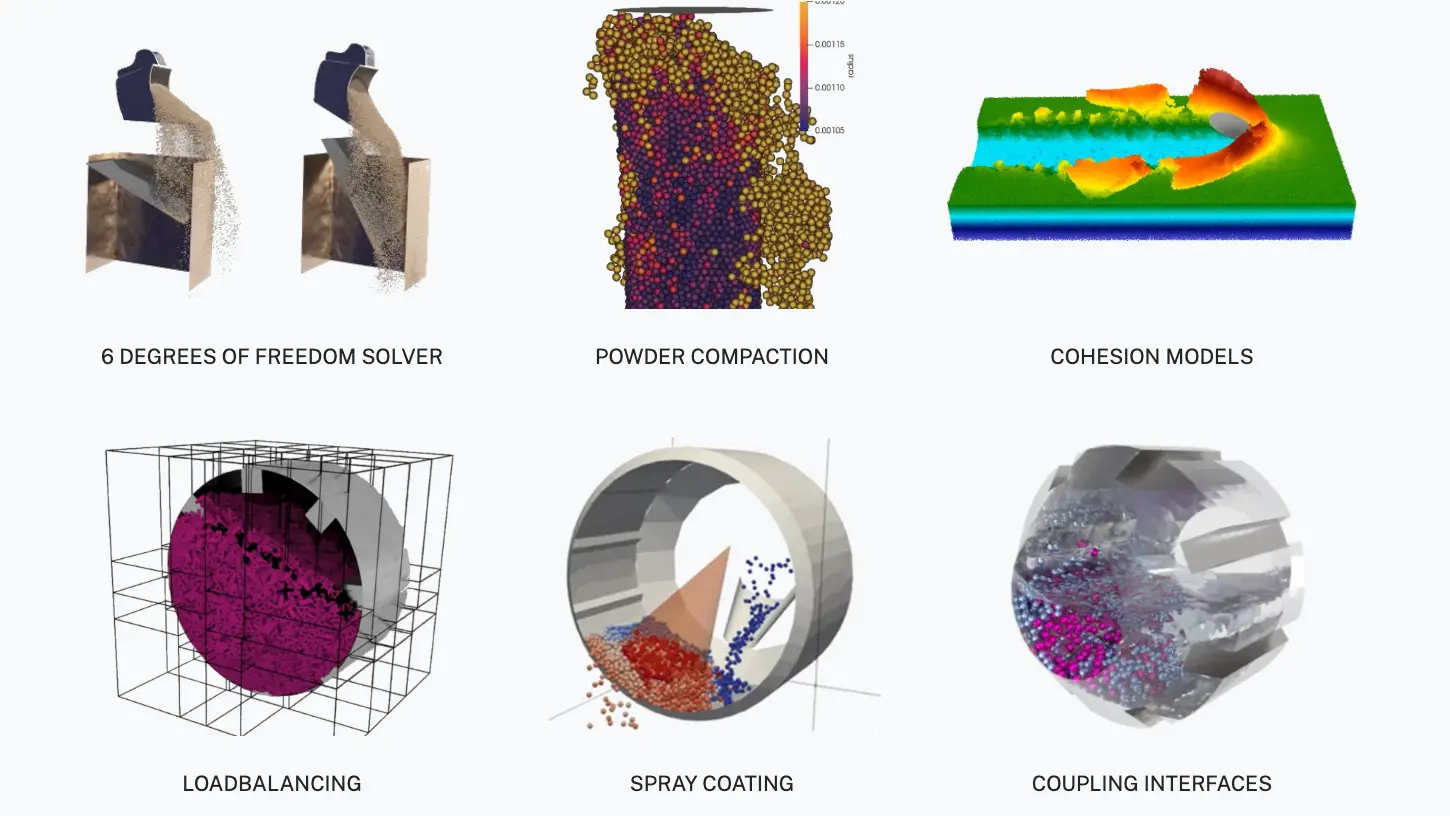
Explore our Features
Discover powerful tools and technologies designed to enhance your simulations.

References
Hear from satisfied customers about the impact our solutions had on their success.
Consultancy
We’ll provide expert answers and introduce our software, always pushing simulation boundaries.